
The pain in the knee is extended can be a symptom of it, which is a signal of problems in the body – the occurrence of diseases of the joints, or just the increased load on the feet.
It is Difficult to find a person who's never experienced the pain in the knees, and in a certain period of time in life. Discomfort, clicking, or a different intensity of pain in the joints of the knee frequently occur in both adults in children, which is due to a number of reasons. The older a man becomes, the greater is the likelihood of a variety of diseases, the first symptom of which is joint pain in my knees. That is, due to the age peculiarities of the body: it slows down the metabolic processes, the wear and tear of the cartilage, the approach of the other problems of the musculoskeletal system, it is found nerves.
Due to the complex anatomical structure of the large structures of the face, with a high-pressure, often in the overloads, the knee joint, so vulnerable. Any damage to the structure of each of the elements, for example, bursal, the lead does a violation of the motor function of the knee, in consequence of the pain, syndrome. Ligaments the menisci is considered to be the most vulnerable, and therefore get injured in 80-85% of cases).
The anatomical structure of the knee
The knee comprises the knee joint at the distal end of the femur in the two condyles podmienkami, tibial bones, muscles, and nerves, is found the ligaments, patella (kneecap), a common handbags within the menisci.
The knee joint is one of the major joints of the body. At the top of the selection of the femur. The articular surface of the lateral (outer) to medial (inner) condyles articulate with the patella into the tibia. In the meniscus, which is the connective tissue of the cartilage serve as shock absorbers of the joint. Thank you for the rational allocation is to the weight of the weight of the tibial plateau in an increasing total stability. The thin, double-headed, paliperidonesee of the other muscles of the sinhroniziruete capsular-ligamentous structures, which provide the motor activity of the knee joint.
The elements of the knee, as related by several ties. In total the inside there are two cruciate ligaments – the back to the front. Podmyshalsky bedernau thus associated with the bones of the bones of the tibia in fibular collateral ligament. Oblique popliteal ligament is located in the back of the Bursa in the knee. Many of the common disturbances is a major on the final day of the capsule does not communicate with the joint. The flow of the blood to the elements of the knee is the result of a network of blood vessels, the innervation – nerve fibers.
Causes of pain in the knee
There are a lot of causes of pain of the knee joint, which can be divided into several groups.
Traumatic injuries of the knee features:
- The damage to the knee. As a result of the rupture of the blood does the veins of the pride of the local bleeding in the soft tissue of the joint. Redness, swelling, nerve damage leads to pain, difficulty of motion.
- A partial or Complete rupture of the ligaments. Often, the diagnosis of a partial violation of the integrity of the internal lateral ligaments, which result from excessive eversion of the tibia towards the outside.
The external ligament is less than the torn interior. It is a consequence of the strong deviation of the tibia inwards from the exposed legs, for example. The way of the cross ties is inevitably accompanied by a hemarthrosis.
A complete rupture of both ligaments is often associated with the joint from the capsule, tearing of the internal meniscus. This injury leads to excessive mobility of the knee joint, accompanied by severe pain intensity, that is, from the level of the subject to rupture.
- Hemarthrosis of the knee joint – the outpouring of blood into the joint cavity. Sometimes, the traumatic non-traumatic in nature. Traumatic hemarthrosis occurs when ruptures meniscus, complete or incomplete rupture of ligaments, intra-articular fractures, contusions of the knee region. A Non-traumatic life of the option is one of the symptoms of the disease, characterized by increased fragility of the walls of the vessel or of the violation of the blood coagulation system. These include hemophilia, scurvy, a severe form of hemorrhagic diathesis. Accumulated in the joint cavity compresses the blood to the tissues, disturbances of the blood circulation in them. The special pigment – hemosiderin – is having a negative impact on the ligaments, hyaline cartilage, synovial bag, which leads to a loss of its elasticity. The result was the defeat of the articular Bursa the swelling of its fibre, in the increased production of joint fluid. Due to the recurrent bleeding becomes, the decline in the total destruction of earth.
- The knee miniscope – a violation of the integrity of the menisci in the knee joint. In-side the outer form of the defective or damaged meniscus, when it is inside the medical. If it is one of the most common, but it is hard to diagnose injuries to the knee joint. At the risk of the disease, which is, therefore, not only the athletes who participate in intense exercise, as well as ordinary people. A meniscus tear can be iz and occur suddenly, in an unusual movement when turning the body, the exposed feet of a strong blow to the knee.
- Patellar luxation – the abnormal shift of the patella. Of the trauma, which is diagnosed in no more than 0,7% of the total cuts. It is Often the case, dislocation of the outer and the inner, rarely, very rarely vertical or torsional. In the case of incomplete dislocation of the patella is fixed on the lateral (outer) condyles, while the outside is full of iz and the lateral condyle.
- Closed-or open-fracture in the knee joint, the upper part of the leg, or the bone of the bone of the lower division of the bedernau. Just take the damage so frequently in combination with injuries to the soft tissues of the knee, causing a massive bleeding, excessive movement in the knee region of the deformation.
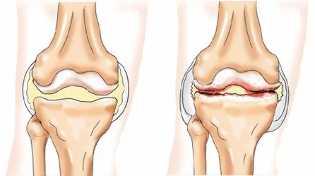
Types of the degenerative-dystrophic diseases of the articular elements of the knee:
- Arthritis – an inflammation of the knee joint. Similar to the mechanism of the development of the pathology in the whole of osteoarthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout (the deposition of urate in the joints).
- Osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis) with injuries to the knee non-inflammatory in nature, affecting all of its structure leads to severe degenerative changes.
- Of Bursitis Bursa synovial inflammation leads to the pain in a flexion-extension movement of the knee.
- Periarthritis of the tendons of the knee – inflammation of the capsule of the goose the feet, knees, tendons, the ligaments of the muscles about the joint. The pain occurs mostly going down, while up and down stairs, especially with heavy loads, and in the focus of the inner surface of the knee.
- The chondropathy patella , degenerative-necrotic changes of the articular cartilage (back) surface of the patella. The rate of destruction may be different from the area of the lung the softening of cracks in the wear and tear.
- Chondromatous the serious nature of the chronic disease, which is caused by dysplastic process in the area, with the island of regeneration of the membrane of the common lupine, and in the cartilage of the gondrom. It is not in the off position, a separate cartilaginous ossification of the organisation.
- Baker's cyst – forming a tight, elastic, rounded tumor mass in the popliteal fossa, which is located on the opposite side of the patella. The cyst is clearly visible in the unbent condition of the knee. Cause discomfort, pain in the region of the popliteal. The considerable size of the compacts may be found in the nerves, leading to disruption of innervation in the blood stream.
- Goff is a disease – a disease which is accompanied by the destruction of the continued decline of the adipose tissue located around the knee joint. The pinching, swelling of the any other damage to the fat cells – adipocytes – end, the replacement of dense fibrous tissue. At the end of a buffer the function of the "fat bag" is broken and the texture becomes very fat are not able to perform the role of a shock absorber.
- A disease Osgood– - schlatter's disease is characterized by necrosis lumpy part of the tibia. The diagnosis of the young people against the 10 to 18 years of age, are involved within the sport. Pod patella appears as a painful lump in the absence of the treatment, which will lead to the restriction of the movement of the foot, or a total of immobilization, the malnutrition of the muscles.
The disease, which may be the irradiation of pain in the knee region:
- Coxarthrosis of the hip – chronic injury to the hip joint, along with the gradual decline of the degenerative changes in it. Often the pain spreads down the outer surface of the femur at the knee or below.
- Neuropathy of the sciatic nerve there is no inflammatory damage to the nerve due to compression or to compression of the spazmirovannah of the blood vessels. If there is a nerve that comes up the leg, starting from the back in the region of the passes through the tailbone into the pelvis. The lock-In On a single point together in the water, or the disturbance of the sense of the pulsating pain.
- Fibromyalgia – extra-articular lesions of the soft tissues of the non-inflammatory nature of the totality of the symptoms, such as arthralgia, muscle weakness, depression, etc.
Some of the systemic diseases, which lead not to the pain in the knees:
- Osteoporosis is a disease of the skeletal system, chronically progressive course, the change of the mineral composition of the bone. "Washout" of calcium from the bones to the water to make their own weakness. The process is accompanied by pain, or the pain in his body.
- Tuberculosis of the bones. Tuberculous lesions of the area of the bones leads to constant severe pain.
- Osteomyelitis is a disease of infectious-inflammatory nature, and affecting all of the elements of the structural bone. The result of such a special, such as, tuberculosis (tb) in a non-specific, often coccal, osteomyelitis become the redness of the skin, swelling, local pain in the bones, in my muscles and febrile temperatures.
- Some of the infectious diseases. When a Player's syndrome, in addition to the involvement of the urogenital tract to the eyes, and the effect on the results. One of the manifestations of Lyme disease is arthralgia.
Kind of a pain in the knees
With regard to etiology, the nature of the intensity of the pain may vary.
- Painful. Arthritis, osteoarthritis.
- A sharp, strong. Break of the elements of the knee, tendon rupture, acute bursitis, injury to the knee, the deterioration of the miniscope, deforming osteoarthritis of the.
- Throbbing. The entire deforming arthrosis, damage to the meniscus.
- Activity. Osteomyelitis.
- Stupid. From bursitis, chronic back Legg.
- Burning. When the compression of the sciatic nerve, tuberculous process in the bone.
- Fire. The pinching of the nerve trunk.
- The pain when walking. After a Baker's cyst, bursitis, arthritis, gonarthrosis, periarthritis.
- The pain of his own. Gout arthritis.
The diagnosis of the disease, which is caused by pain in the knees
Physical examination:
- a history of the complaint;
- the visual is the main palpation of the knee.
Laboratory text:
- biochemical the clinical blood test;
- serological major to the blood;
- the immunological analysis of the blood;
- rheumatologic samples;
- bacteriological analyse the synovial fluid.
Invasive instrumental methods:
- arthroscopy;
- the puncture of the joint capsule;
- a needle, a biopsy of the bone.
The non-invasive diagnosis:
- radiography in a knee joint;
- densitometry;
- to check the main joint;
- An MRI, a CT scan or an.
The treatment of pain in the knee
If the pain in one or both of the knee non-traumatic nature of the phenomenon, it would be moral to go for the first time, to the therapist, who, on the basis of the patient's complaints objective, the results of the review, just sent to a specialist-orthopedist, a rheumatologist, neurologist, or a phlebologist. In any knee injury, you will need to contact the doctor, or the traumatologist-orthopedist.
Treatment in each and every case is different, depending on the cause of the pain, i.e. the injury or disease. For each and every illness has its own regime of treatment. But first, you must be patient to follow some General rules:
- a significantly shorten the duration of the walk-in-themselves on their feet all day long;
- students on a temporary basis (until recovery) to abandon the training of the ordinary people of the iz, running, or jumping;
- when you increase the pain to completely dispense with the motion he gave at the knees for a distance, the elastic bandages;
- wear a brace or wrap does not immobilize the knee joint;
- the injury of cold while on the site of the injury to the exposure.
Rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, systemic auto-immune disease is in a serious need of a comprehensive treatment for a number of months. The primary therapy consists of immunosuppressive drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory in the of the hormonal drugs, gold preparations, etc.
Bursitis used In the treatment of medication to relieve pain in an anti-inflammatory medication. If there is any evidence of infection, a course of antibiotics. Therapeutic puncture of the bags is carried out to remove the excess fluid from the synovial cavity, and/or review of corticosteroids. Chronic inflammation of the Bursa can help you to get rid of the surgery – surgical bunion surgery.
Once inside the deforming osteoarthritis of the effective articular injections of corticosteroids, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and in chondroprotectors. A local Of pain is called compresses with Dimexidum, or bischofite, creams, in gels with anti-inflammatory action. Help massage, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises. A serious injury requiring surgery of the knee – arthroplasty of the hip joint.
Treatment for osteoporosis is taking bisphosphonates, calcitonin, calcium, vitamin D, etc.
The treatment of meniscus tears conservative or surgical. Conservative treatment consists of the use of analgesics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, hyaluronic acid, chondroprotectors. But first of all to produce such a joint.
The type of surgical intervention:
- meniscectomy;
- partial (partial) meniscectomy;
- transplantation of the meniscus;
- arthroscopy;
- arthroscopic suture of the torn meniscus.
In the case of an injury of the knee after treatment, is very important for the period of rehabilitation, which is expected to take place under the supervision of a physical therapist or a podiatrist. The doctor will be in the optimal recovery of joint function. The main methods of postoperative rehabilitation are to be considered, massage, medical gymnastics. An efficient knowledge even of the particular simulators, the gradual development of the condition.













































